
There are two major strands to position of traditional publishers have taken in justifying the process by which they will make the, now inevitable, transition to a system supporting Open Access.

There are two major strands to position of traditional publishers have taken in justifying the process by which they will make the, now inevitable, transition to a system supporting Open Access.

Understanding how a process looks from outside our own echo chamber can be useful. It helps to calibrate and sanity check our own responses. It adds an external perspective and at its best can save us from our own overly fixed ideas. In the case of the ongoing Elsevier Boycott we even have a perspective that comes from two opposed directions.

When the history of the Research Works Act, and the reaction against it, is written that history will point at the factors that allowed smart people with significant marketing experience to walk with their eyes wide open into the teeth of a storm that thousands of people would have predicted with complete confidence. That story will detail two utterly incompatible world views of scholarly communication.

Image via Wikipedia Last Friday I spoke at the STM Innovation Seminar in London, taking in general terms the theme I’ve been developing recently of focussing on enabling user discovery rather than providing central filtering, of enabling people to act as their own gatekeeper rather than publishers taking that role on for themselves.

I recently made the most difficult decision I’ve had to take thus far as a journal editor. That decision was ultimately to accept the paper; that probably doesn’t sound like a difficult decision until I explain that I made this decision despite a referee saying I should reject the paper with no opportunity for resubmission not once, but twice.

The idea that “it’s not information overload, it’s filter failure” combined with the traditional process of filtering scholarly communication by peer review prior to publication seems to be leading towards the idea that we need to build better filters by beefing up the curation of research output before it is published.

There has been an awful lot recently written and said about author-pays business models for scholarly publishing and a lot of it has focussed on PLoS ONE. Most recently Kent Anderson has written a piece on Scholarly Kitchen that contains a number of fairly serious misconceptions about the processes of PLoS ONE.

Suddenly it seems everyone wants to re-imagine scientific communication. From the ACS symposium a few weeks back to a PLoS Forum, via interesting conversations with a range of publishers, funders and scientists, it seems a lot of people are thinking much more seriously about how to make scientific communication more effective, more appropriate to the 21st century and above all, to take more advantage of the power of the web.
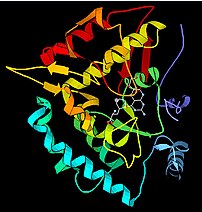
A story of two major retractions from a well known research group has been getting a lot of play over the last few days with a News Feature (1) and Editorial (2) in the 15 May edition of Nature. The story turns on claim that Homme Hellinga’s group was able to convert the E. coli ribose binding protein into a Triose phosphate isomerase (TIM) using a computational design strategy.

Image via Wikipedia Once again a range of conversations in different places have collided in my feed reader. Over on Nature Networks, Martin Fenner posted on Researcher ID which lead to a discussion about attribution and in particular Martin’s comment that there was a need to be able to link to comments and the necessity of timestamps.