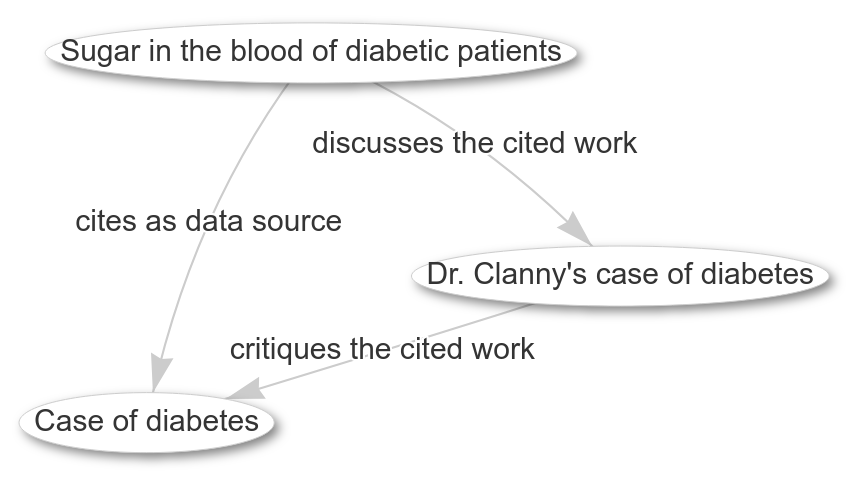
Diabetes was already discussed in literature back in 1838-1839 (doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)96038-1, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)96066-6, and doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)83966-6). These three papers show a short discussion.

Diabetes was already discussed in literature back in 1838-1839 (doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)96038-1, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)96066-6, and doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)83966-6). These three papers show a short discussion.
This summer I am trying to finish up some smaller projects that I did not have time for to finish, with mixed successes. I am combing this with a nice Dutch staycation, and I already cycled in Overijssel and in south-west Friesland and learning about their histories. But this post is about an update on my Citation Typing Ontology use cases. And I have to say, a mention by Silvio Peroni is pretty awesome, thanks! First, the bad news.
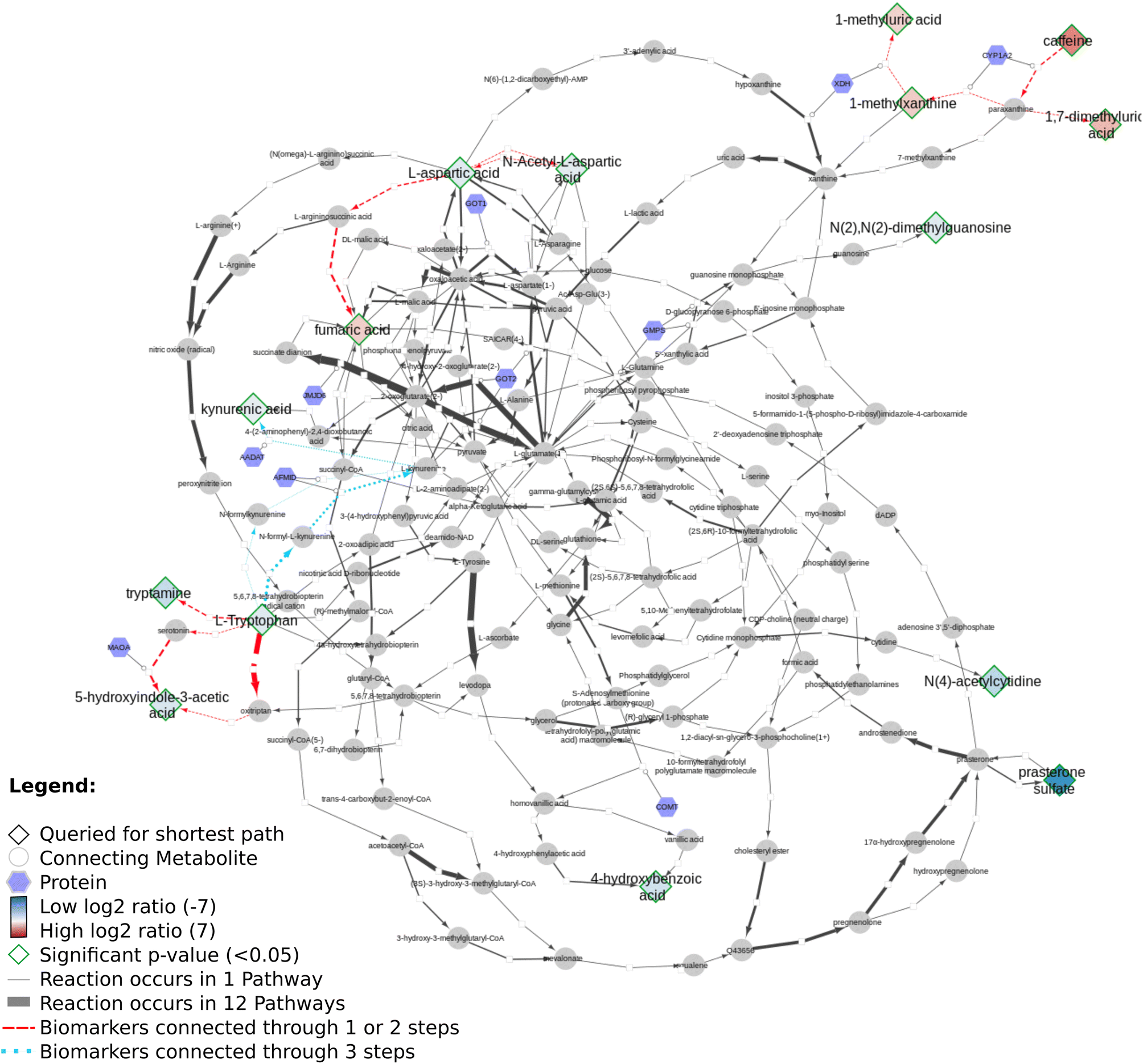
I am still catching up with a lot of work, and found out I actually had forgotten to blog about this cool article by Denise Slenter: “Discovering life’s directed metabolic (sub)paths to interpret human biochemical markers using the DSMN tool” (doi:10.1039/D3DD00069A). This paper explains how various open science resources (Wikidata, Reactome, WikiPathways) are used to visualize the biological story of the data from two metabolomics experiments

About a year ago I started migrating my blogger.com blog to a git-version-controlled, Markdown-based blogging platform. I have to say, it has been a happy year. It actually is awesome to port old blog posts (follow that here) and to see what I have been working on some 17, 18 years ago. I do have a nasty bug to fix that causes the conversion of the Markdown to HTML is scaling badly.

In the CDK2024 grant we wrote about updating various software projects using the Chemistry Development Kit. We even wrote that “[r]equired API changes will be publicly shared and disseminated with the Groovy Cheminformatics with the Chemistry Development Kit book (egonw.github.io/cdkbook/)”. The Groovy Cheminformatics with the Chemistry Development Kit book is a project that has run since 2009.
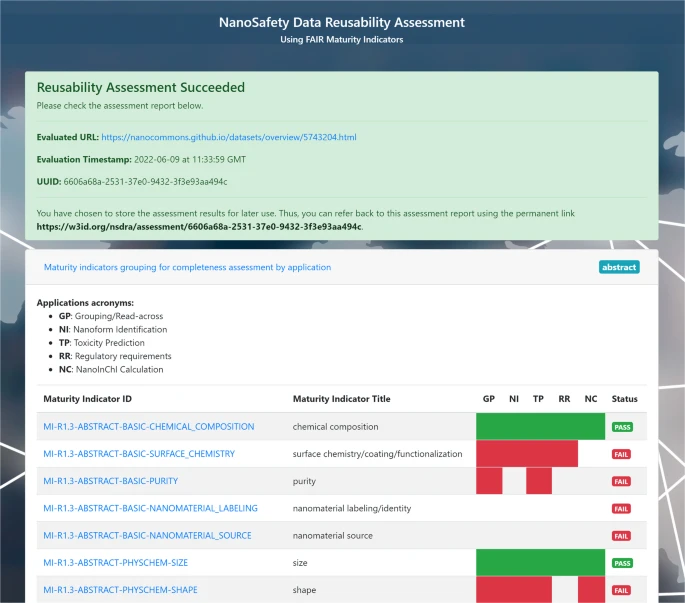
Ammar is finishing up his PhD thesis with his research on the use of FAIR towards predictive toxicology. Or, “AI ready”, as the term FAIR is now sometimes explained. Any computational method needs good data, and just FAIR is not enough. It needs to meet community standards, as formalized in R1.3. To me, this includes meeting community standards like minimal reporting standards.
Noting that in the coming week I am not attending the ELIXIR All Hands in Uppsala. Having lived in (and around) Uppsala for more than three years, I am disappointed and with the first stories from colleagues coming in even more. But it has been a way too busy year, I have much to finish up, and I need to take care of myself too. I am not 32 anymore. But in the past two weeks I did attend two workshops.
I was about to call this blog post From spreadsheets to RDF , after the post last week. But then I decided to just use the pattern I typically use. Why I wanted to use that shorter term in the first place was that one of the thing I like about the AMBIT software (of OpenTox and eNanoMapper fame) is its RDF support (see doi:10.1186/1756-0500-4-487). But RDF, ontologies, those are hard things.

Making something FAIR is hard, particularly when you do more than making something findable. We’ve seen before that making something usefully findable requires deep indexing, and already that continues to be difficult, because we are not seeing it enough. So, when I thought convert a paper led by Hoet’s lab in Leuven into machine-actionable RDF to make it FAIR, I gravely underestimated the amount of work.
Publishing grant proposal is still not very common. The proposal published in Research Ideas and Outcomes) (doi:10.3897/rio.10.e124884) for the NWO Open Science grant for the CDK is, however, not the first and hopefully not the last. Interestingly, it is already cited in (the German) Wikipedia. It is used there to support a statement which tools use the Chemistry Development Kit.