More and more R packages access resources on the web, and play crucial roles in workflows.Examples from the rOpenSci suite of packages include rromeo, GSODR, qualtRics, rnassqs, and many, many others.Like for all other packages, appropriate unit testing can make them more robust.However, unit testing of these packages can bring special challenges: dependence of tests on a good internet connection, testing in the absence of authentication
babette 1 is a package to work with BEAST2 2 ,a software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis from R. babette is a spin-off of my own academic research.As a PhD I work on models of diversification: mathematical descriptionsof how species form new species.
In May 2019 version 0.2.0 of tidync was approved by rOpenSci and accepted to CRAN. Here we provide a quick overview of the typical workflow with some pseudo-code for the main functions in tidync. This overview is enough to read if you just want to try out the package on your own data.
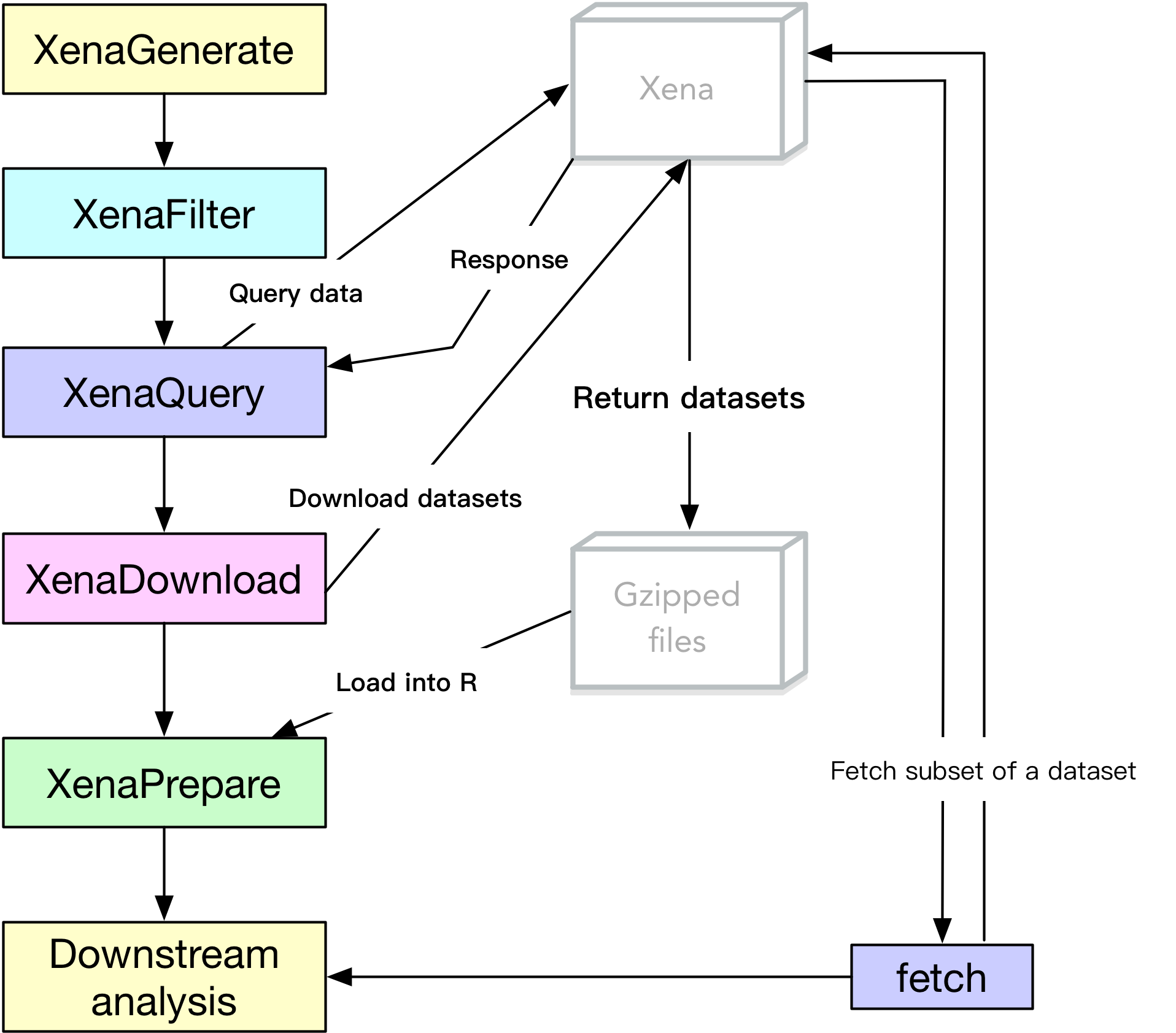
The UCSC Xena platform provides an unprecedented resource for public omics data from big projects like The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), however, it is hardfor users to incorporate multiple datasets or data types, integrate the selected data withpopular analysis tools or homebrewed code, and reproduce analysis procedures.
Teaching collaborative software development In the University of British Columbia’s Master of Data Science program one of the courses we teach is called Collaborative Software Development, DSCI 524. In this course we focus on teaching how to exploit practices from collaborative software development techniques in data scientific workflows.
Software is maintained by people. While software can in theory live on indefinitely, to do so requires people. People change jobs, move locations, retire, and unfortunately die sometimes. When a software maintainer can no longer maintain a package, what happens to the software? Because of the fragility of people in software, in an ideal world a piece of software should have as many maintainers as possible.
We’ve been following rOpenSci’s work for a long time, and we use several packages on a daily basis for our scientific projects, especially taxize to clean species names, rredlist to extract species IUCN statuses or [treeio](many probs with this post) to work with phylogenetic trees.rOpensci is a perfect incarnation of a vibrant and diverse community where people learn and develop new ideas, especially regarding scientific packages.We’ve also
Introduction ramlegacy is a new R package to download, cache and read in all the different versions of the RAM Legacy Stock Assessment Database, a public database containing stock assessment results of commercially exploited marine populations from around the world.
rOpenSci is one of the first organizations in the R community I ever interacted with, when I participated in the 2016 rOpenSci unconf. I have since reviewed several rOpenSci packages and been so happy to be connected to this community, but I have never submitted or maintained a package myself. All that changed when I heard the call for a new maintainer for the qualtRics package. “IT’S GO TIME,” I thought.

Stefanie Butland, rOpenSci Community Manager Some things are just irresistible to a community manager – PhD student Hugo Gruson’s recent tweets definitely fall into that category.