The previous post contained an exploration of the anomeric effect as it occurs at an atom centre X for which the effect is manifest in crystal structures.
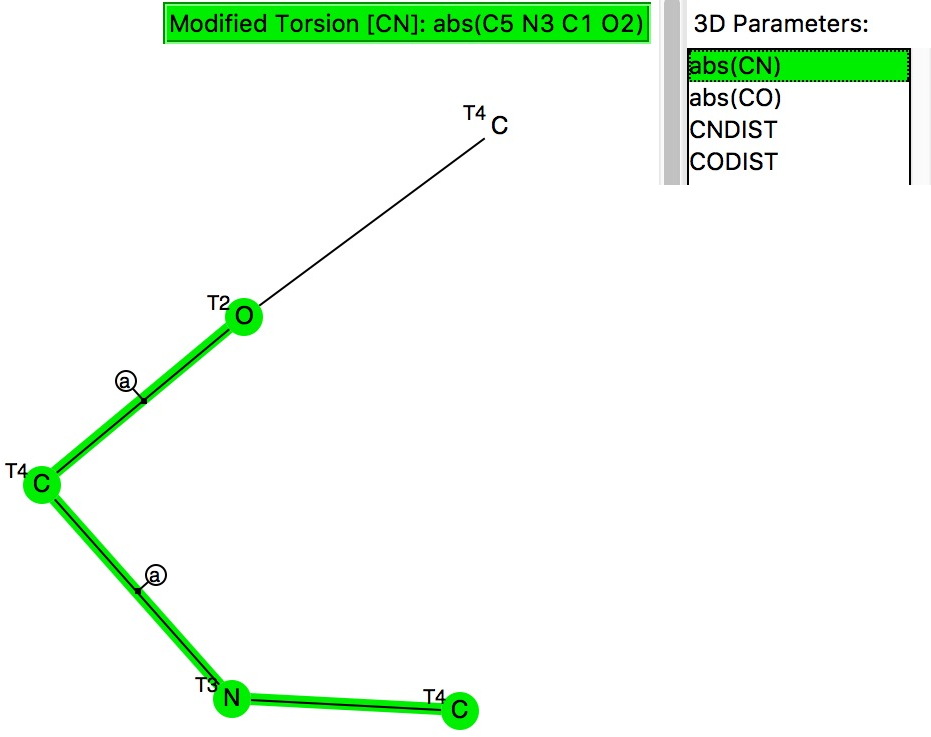
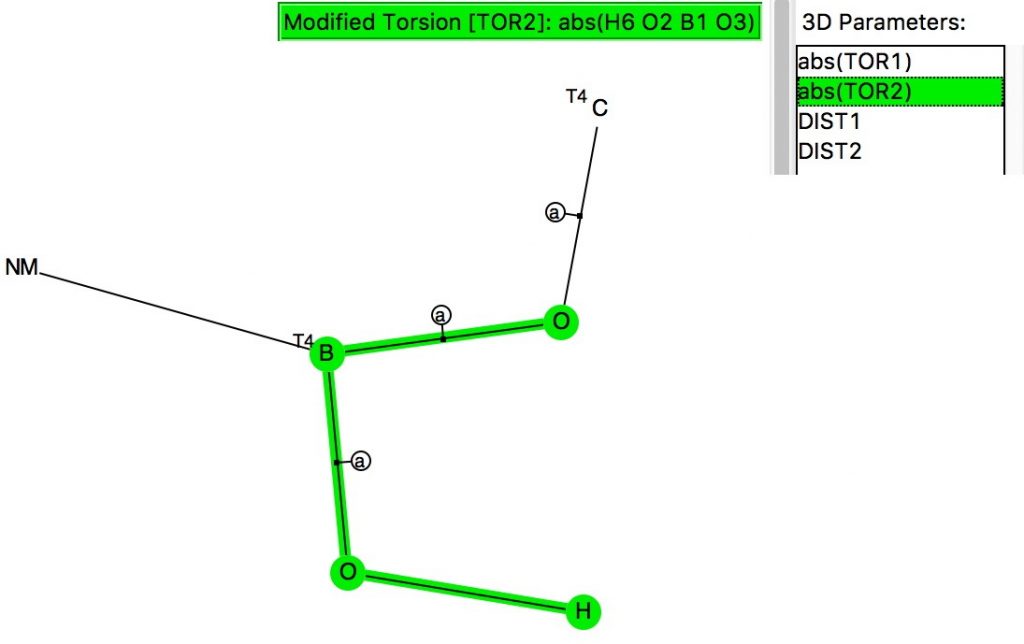
The previous post looked at anomeric effects set up on centres such as B, Si or P, and involving two oxygen groups attached to these atoms.
The anomeric effect occurs at 4-coordinate (sp 3 ) carbon centres carrying two oxygen substituents and involves an alignment of a lone electron pair on one oxygen with the adjacent C-O σ*-bond of the other oxygen. Here I explore whether other centres can exhibit the phenomenon.
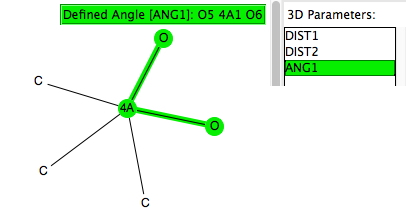
This is a follow-up to one aspect of the previous two posts dealing with nucleophilic substitution reactions at silicon. Here I look at the geometries of 5-coordinate compounds containing as a central atom 4A = Si, Ge, Sn, Pb and of the specific formula C 3 4AO 2 with a trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
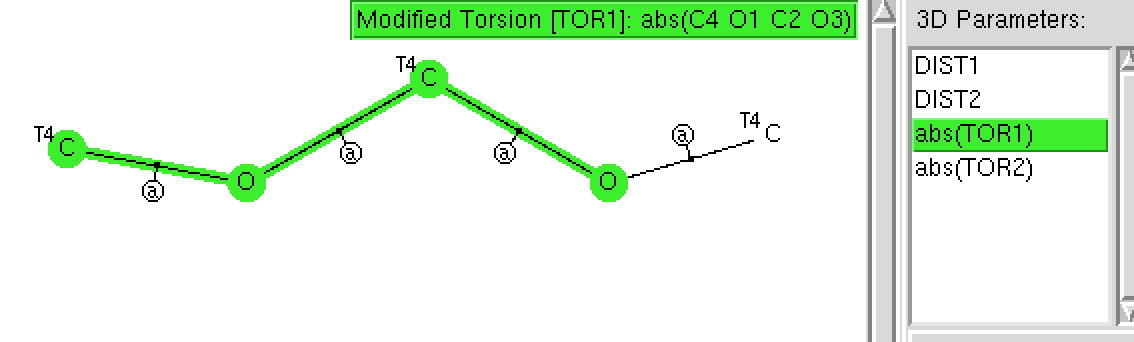
The anomeric effect is best known in sugars, occuring in sub-structures such as RO-C-OR. Its origins relate to how the lone pairs on each oxygen atom align with the adjacent C-O bonds. When the alignment is 180°, one oxygen lone pair can donate into the C-O σ* empty orbital and a stabilisation occurs. Here I explore whether crystal structures reflect this effect.
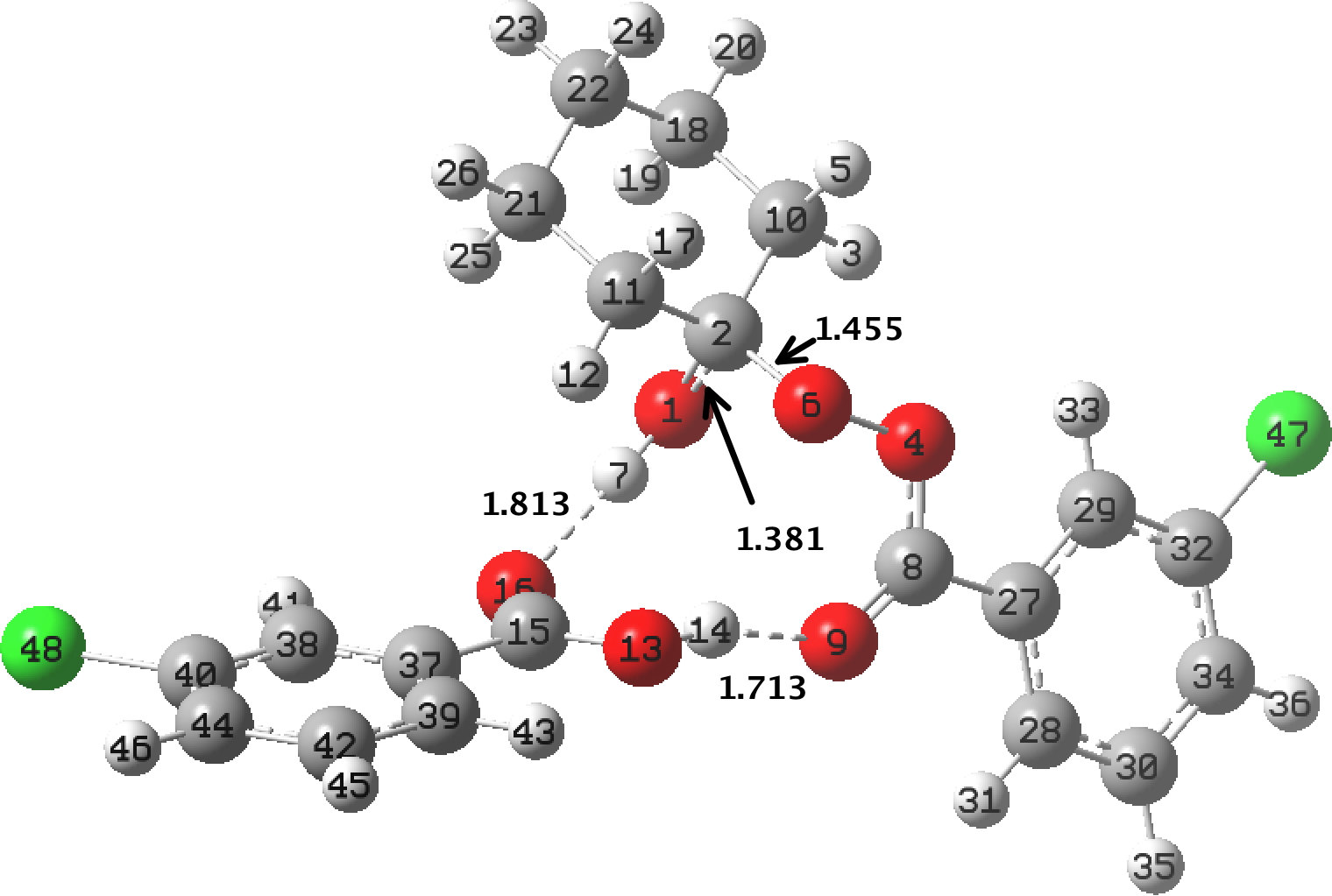
In the preceding post, I discussed the reaction between mCPBA (meta-chloroperbenzoic acid) and cyclohexanone, resulting in Baeyer-Villiger oxidation via a tetrahedral intermediate (TI). Dan Singleton, in whose group the original KIE (kinetic isotope measurements) were made, has kindly pointed out on this blog that his was a mixed-phase reaction, and that mechanistic comparison with homogenous solutions may not be

The title of this post merges those of the two previous ones. The tunable C-Cl bond brought about in the molecule tris(amino)chloromethane by anomeric effects will be probed using the Laplacian of the electronic density.
