My name is displayed pretty prominently on this blog, but it is not always easy to find out who the real person is behind many a blog. In science, I am troubled by such anonymity.

This is rather cranking the handle, but taking my previous post and altering the search definition of the crystal structure database from 4- to 5-coordinate metals, one gets the following. Fe … Co … Ni … Cu … Trigonal bipyramidal coordination has angles of 90, 120 and 180°. Square pyramidal has no 120° angles, and the 180° angles might be somewhat reduced.
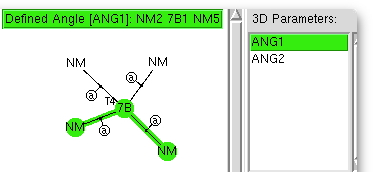
I love experiments where the insight-to-time-taken ratio is high. This one pertains to exploring the coordination chemistry of the transition metal region of the periodic table; specifically the tetra-coordination of the series headed by Mn-Ni. Is the geometry tetrahedral, square planar, or other? One can get a statistical answer in about ten minutes. The (CCDC database) search definition required is shown above.
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate reacts with carbon dioxide to produce 3-keto-2-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate as the first step in the biochemical process of carbon fixation.

I have just noticed unexpected links between two old posts, one about benzene, one about diphenyl magnesium and a link to August Kekulé. † Click for 3D The post about benzene dealt with the apparently simple issue of why all the C-C bonds are of equal length. The answer, in brief is purely because of the σ-electrons. If the π-electrons had their way, benzene would have three short and three long C-C bonds.
The journal of chemical education can be a fertile source of ideas for undergraduate student experiments. Take this procedure for asymmetric epoxidation of an alkene.[cite]10.1021/ed077p271[/cite] When I first spotted it, I thought not only would it be interesting to do in the lab, but could be extended by incorporating some modern computational aspects as well.
Around 100 tons of the potent antimalarial artemisinin is produced annually; a remarkable quantity given its very unusual and fragile looking molecular structure (below). When I looked at this, I was immediately struck by a thought: surely this is a classic molecule for analyzing stereoelectronic effects (anomeric and gauche). Here this aspect is explored.
Science is rarely about a totally new observation or rationalisation, it is much more about making connections between known facts, and perhaps using these connections to extrapolate to new areas (building on the shoulders of giants, etc). So here I chart one example of such connectivity over a period of six years.
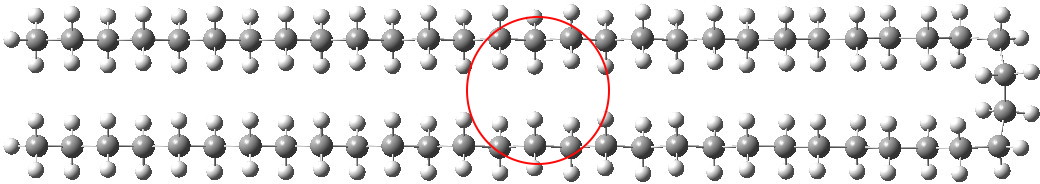
In the previous post, I showed how modelling of unbranched alkenes depended on dispersion forces. When these are included, a bent (single-hairpin) form of C 58 H 118 becomes lower in free energy than the fully extended linear form. Here I try to optimise these dispersion forces by adding further folds to see what happens.

By about C 17 H 36 , the geometry of “cold-isolated” unbranched saturated alkenes is supposed not to contain any fully anti-periplanar conformations.
OK, you have to be British to understand the pun in the title, a famous comedy skit about four candles. Back to science, and my mention of some crystal data now having a DOI in the previous post. I thought it might be fun to replicate the contents of one of my ACS slides here. Firstly, a DOI is one implementation of a more generic (and quite old) concept known as a Handle. This is one form of a persistent digital identifier.