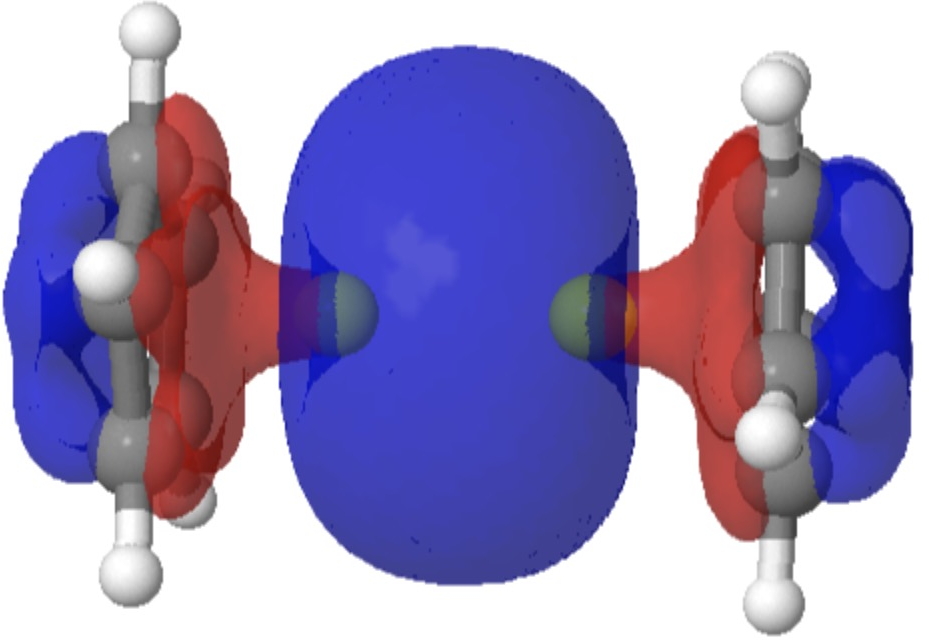
Following on from my template exploration of the Wilkinson hydrogenation catalyst, I now repeat this for the Grubbs variant of the Alkene metathesis reaction. As with the Wilkinson, here I focus on the stereochemistry of the mechanism as first suggested by Chauvin, an aspect lacking in eg the Wikipedia entry.
In the late 1980s, as I recollected here the equipment needed for real time molecular visualisation as it became known as was still expensive, requiring custom systems such as Evans and Sutherland PS390 workstations.

On 24th January 1984, the Macintosh computer was released, as all the media are informing us. Apparently, some are still working. I thought I would give my own personal recollections of that period.
Geoffrey Wilkinson first reported his famous work on the hydrogenation catalyst that now bears his name in 1965 and I met him at Imperial College around 1969 and again when I returned there in 1977.
First, a very brief history of scholarly publishing, starting in 1665 when scientific journals started to be published by learned societies.
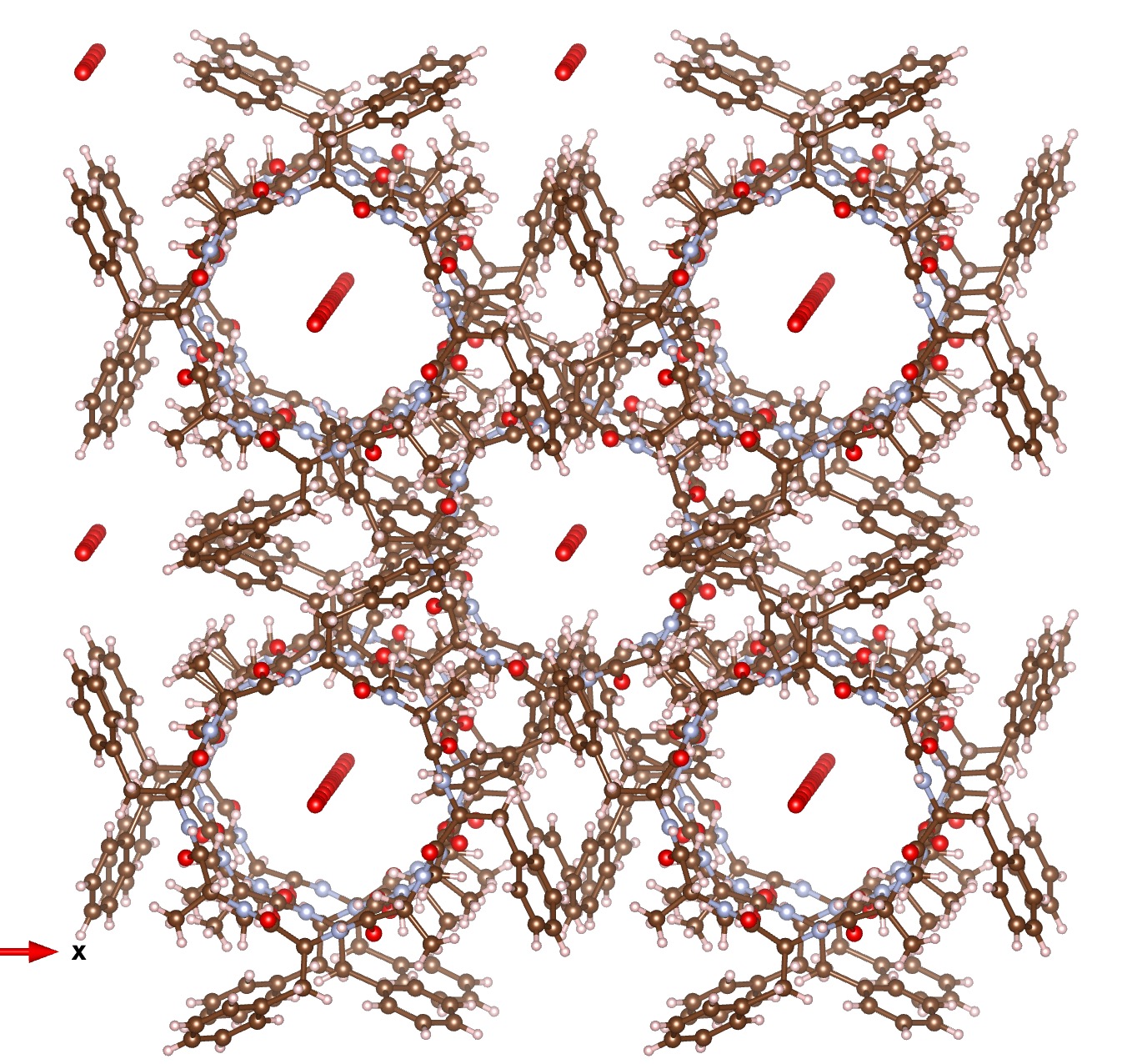
Zosurabalbin,, is receiving a great deal of attention as a new class of antibiotic which can target infections for which current treatment options are inadequate.
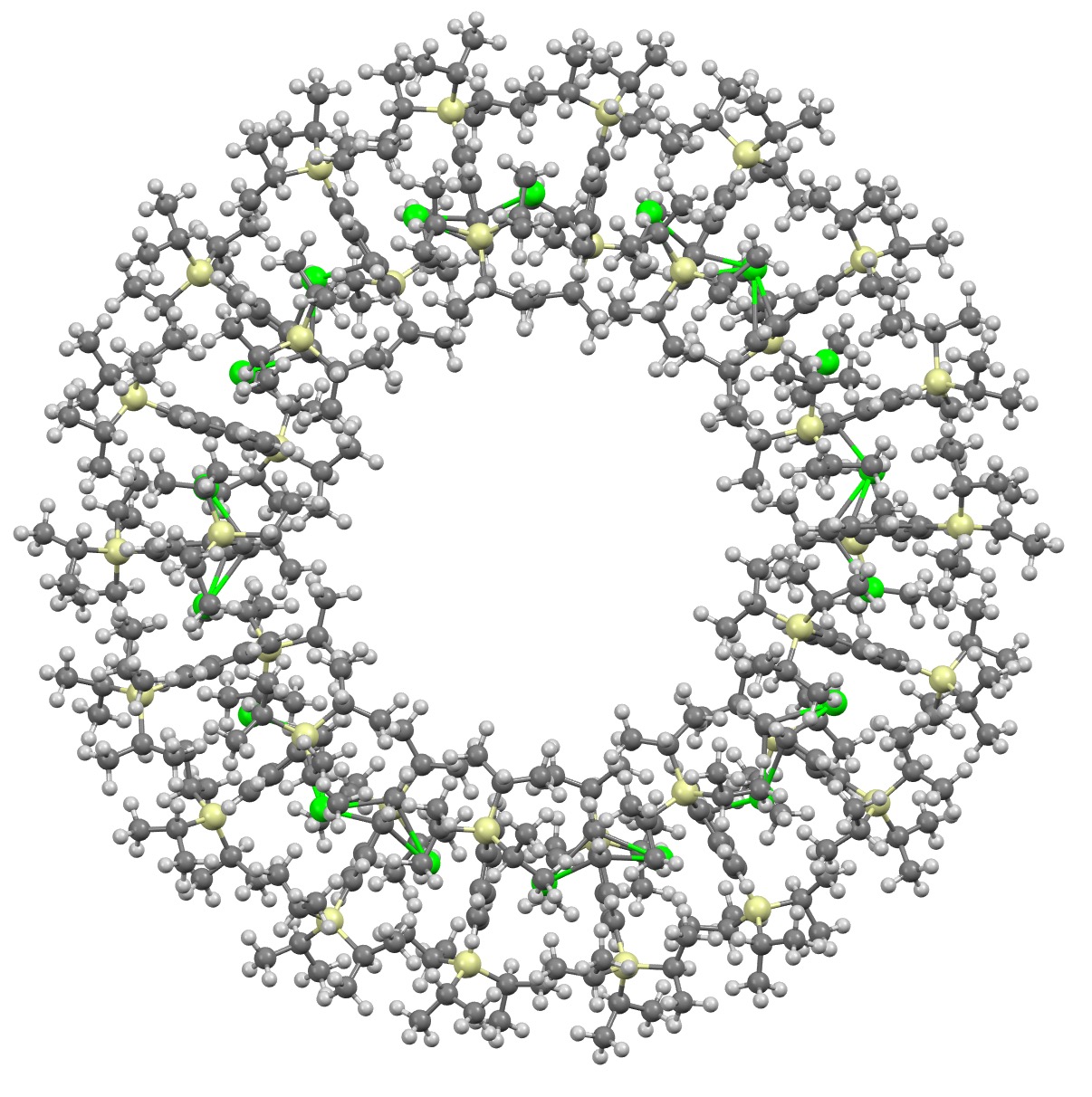
I will approach this example of a molecule-of-the-year candidate – in fact the eventual winner in the reader poll – from the point of view of data. Its a metallocene arranged in the form of a ring comprising 18 sub-units.
The Science education unit at the ACS publication C&EN publishes its list of molecules of the year (as selected by the editors and voted upon by the readers) in December. Here are some observations about three of this year’s batch.
Around 1996, journals started publishing what became known as “ESI” or electronic supporting information, alongside the articles themselves, as a mechanism for exposing the data associated with the research being reported and exploiting some of the new opportunities offered by the World Wide Web.
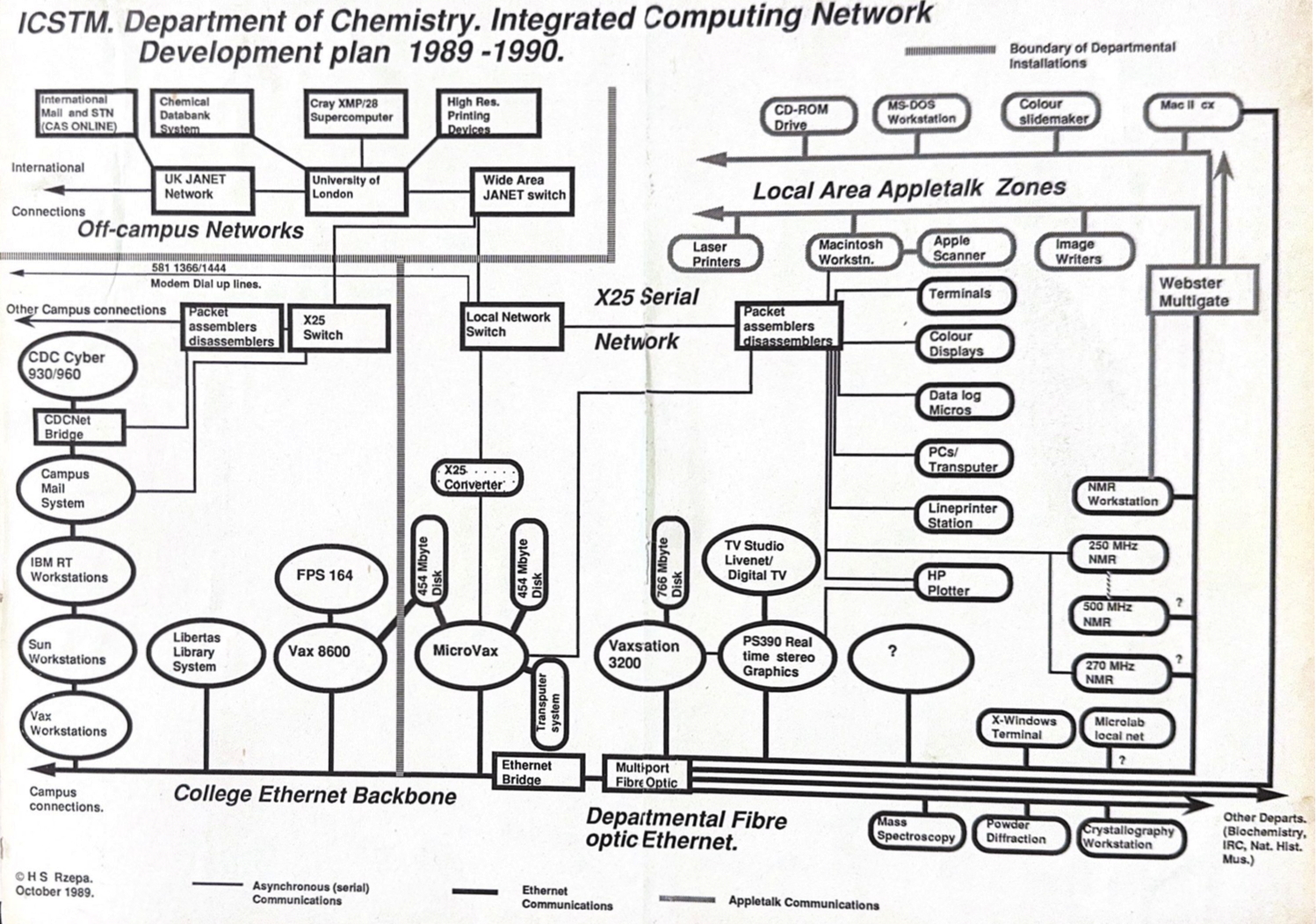
In 2023, we very much take for granted that everyone and pretty much everything is online. But it was not always so and when I came across an old plan indicating how the chemistry department at Imperial College was connected in 1989, I was struck by how much has happened in the 34 years since.
I am a member of the Royal Society of Chemistry’s Historical group. Amongst other activities, it publishes two editions of a newsletter each year for its members.