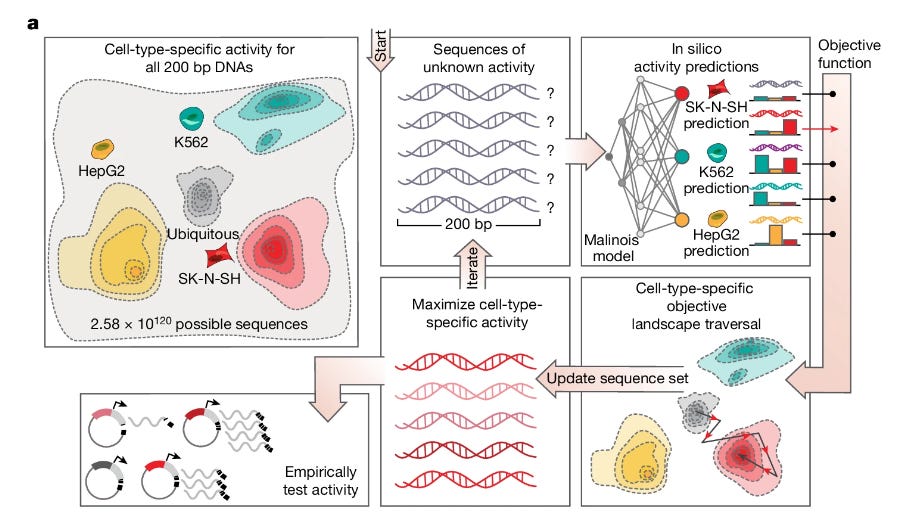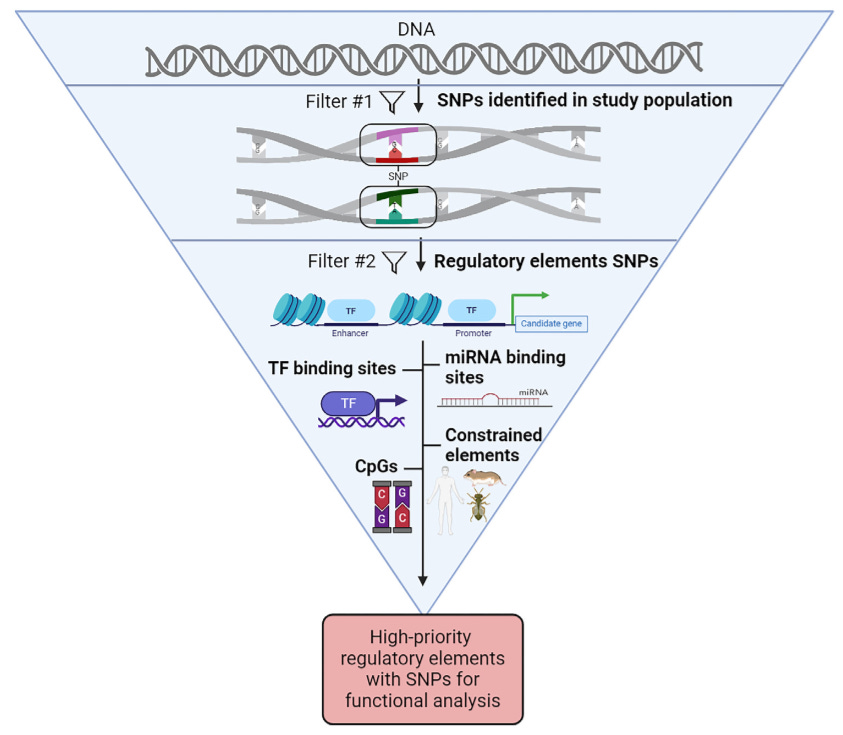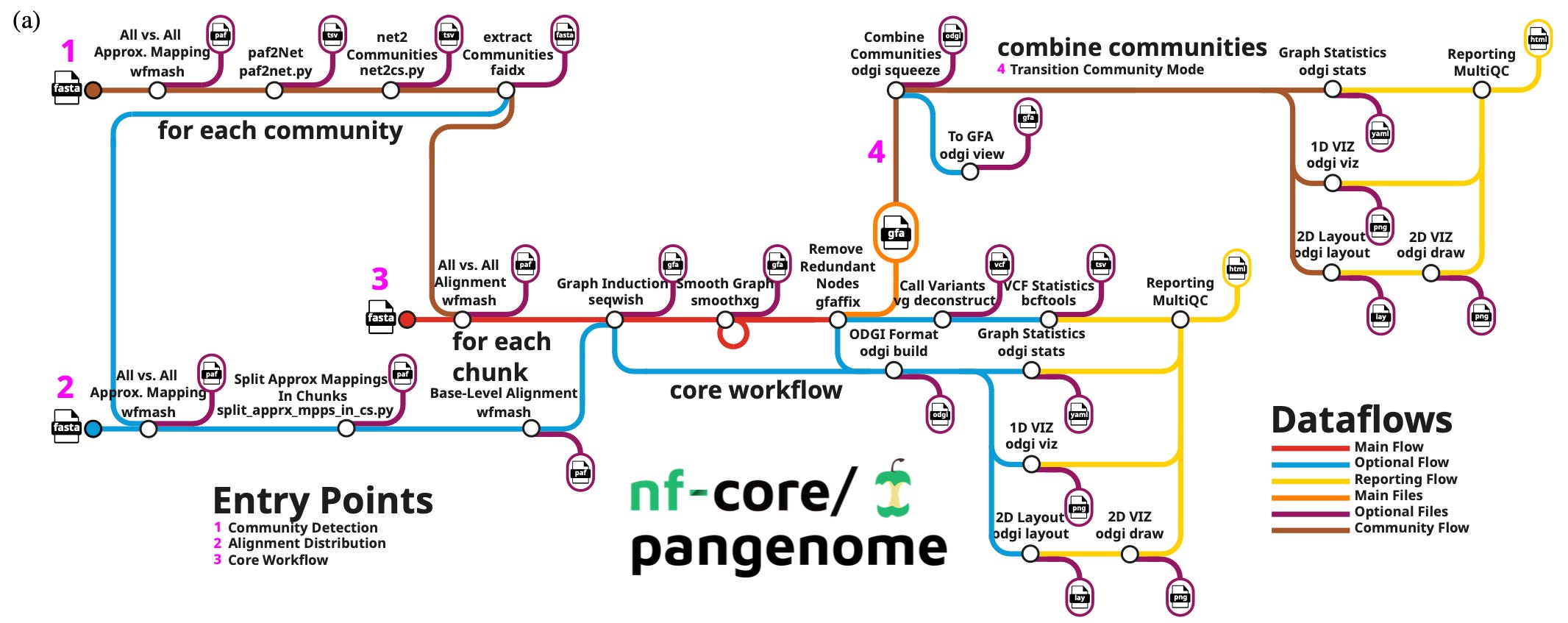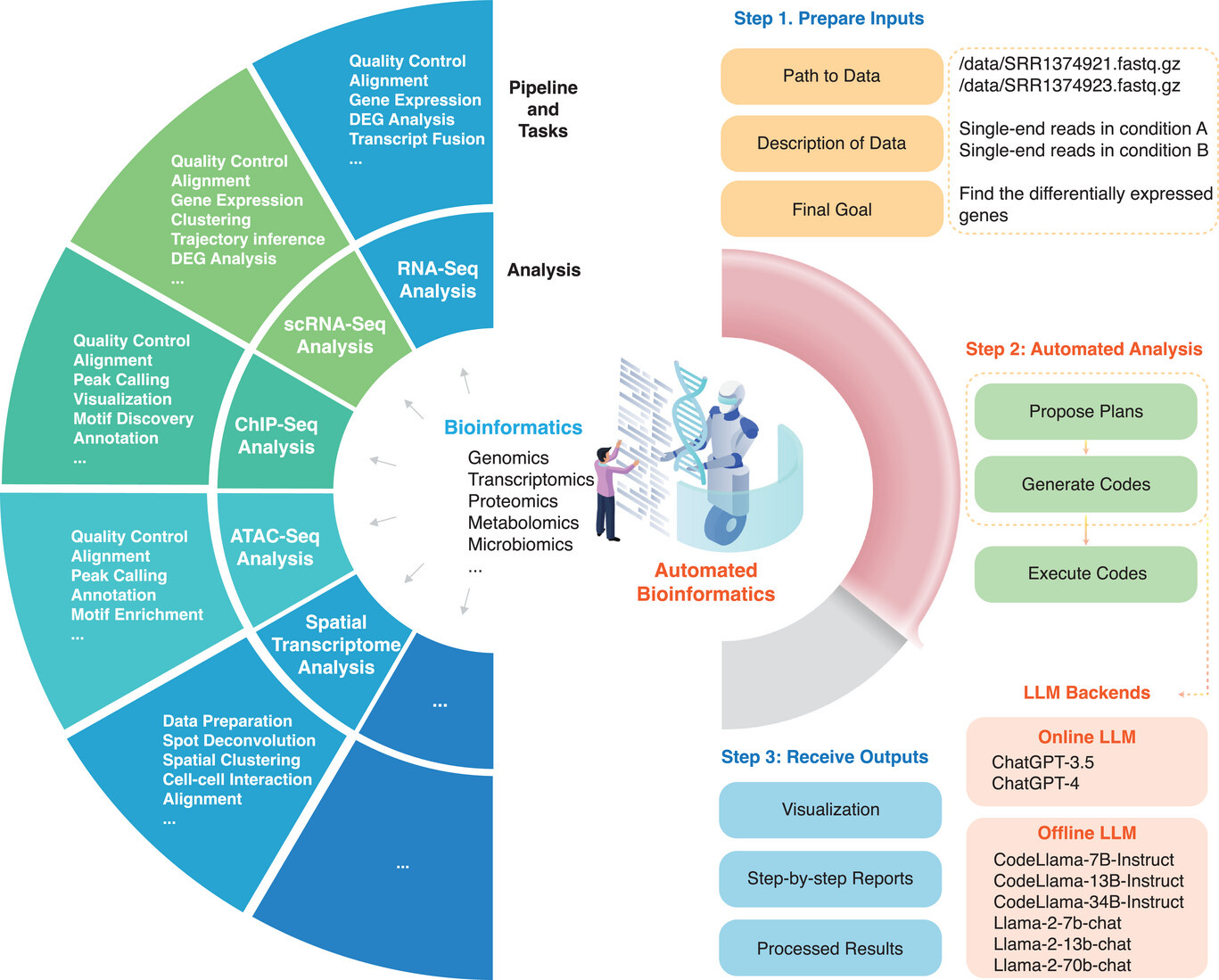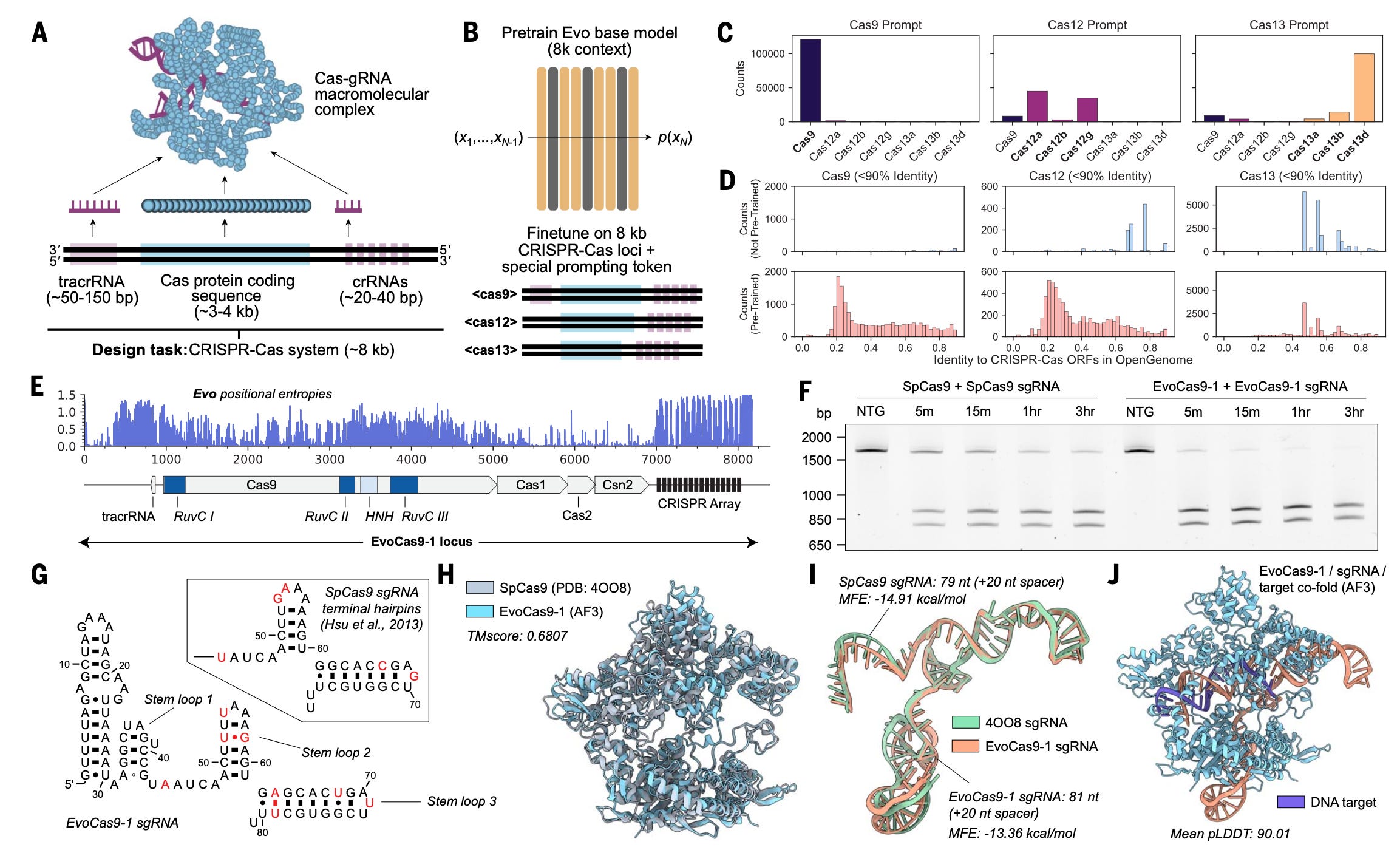
This week’s recap highlights the Evo model for sequence modeling and design, biomedical discovery with AI agents, improving bioinformatics software quality through teamwork, a new tool from Brent Pedersen and Aaron Quinlan (vcfexpress) for filtering and formatting VCFs with Lua expressions, a new paper about the NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog, and a review paper on designing and engineering synthetic genomes.