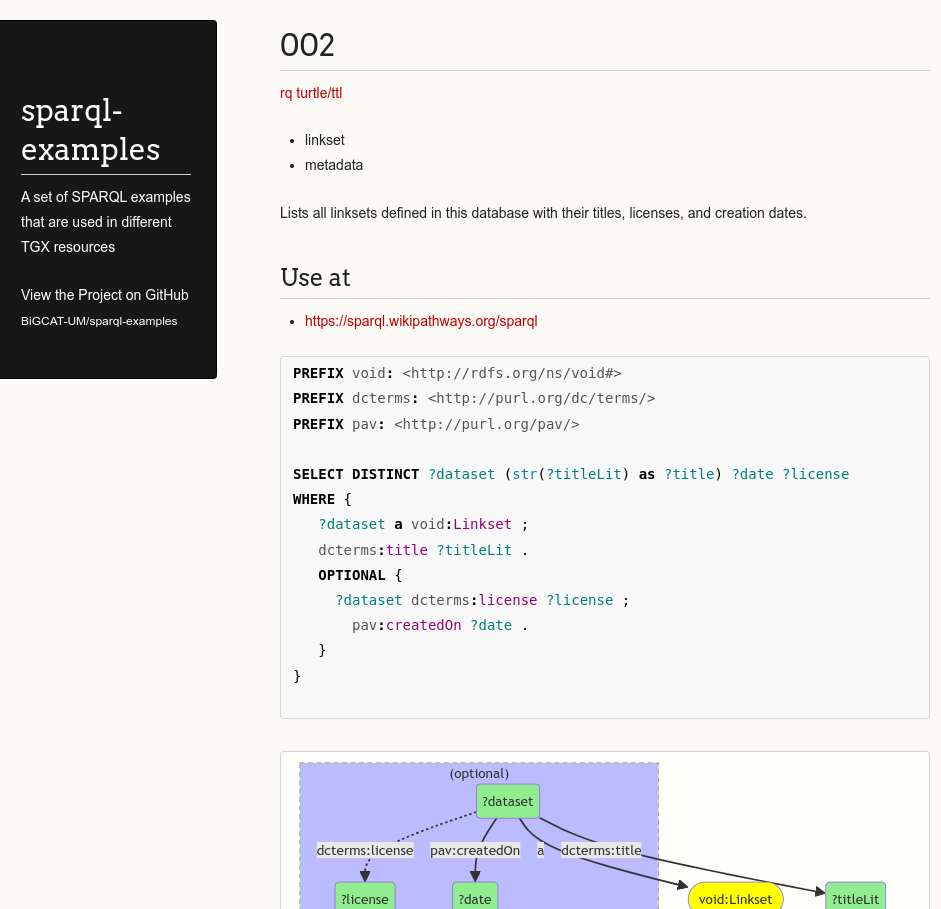
Jerven Bolleman et al. recently published a great preprint about how to use RDF to give SPARQL queries context by linking it (semantically) with metadata. The context includes keywords, the SPARQL endpoint the query can be run against, and a human-oriented description of the query.