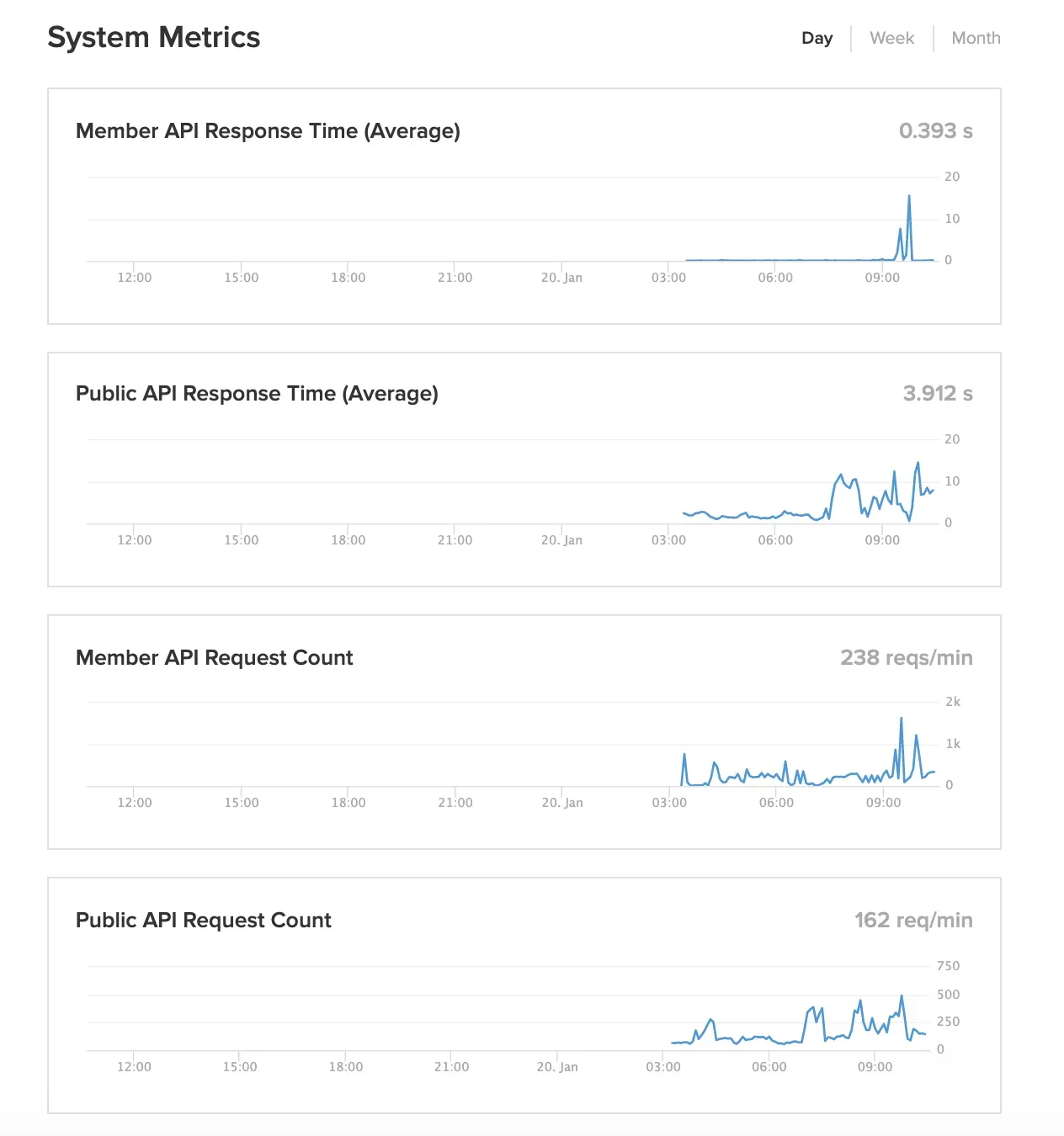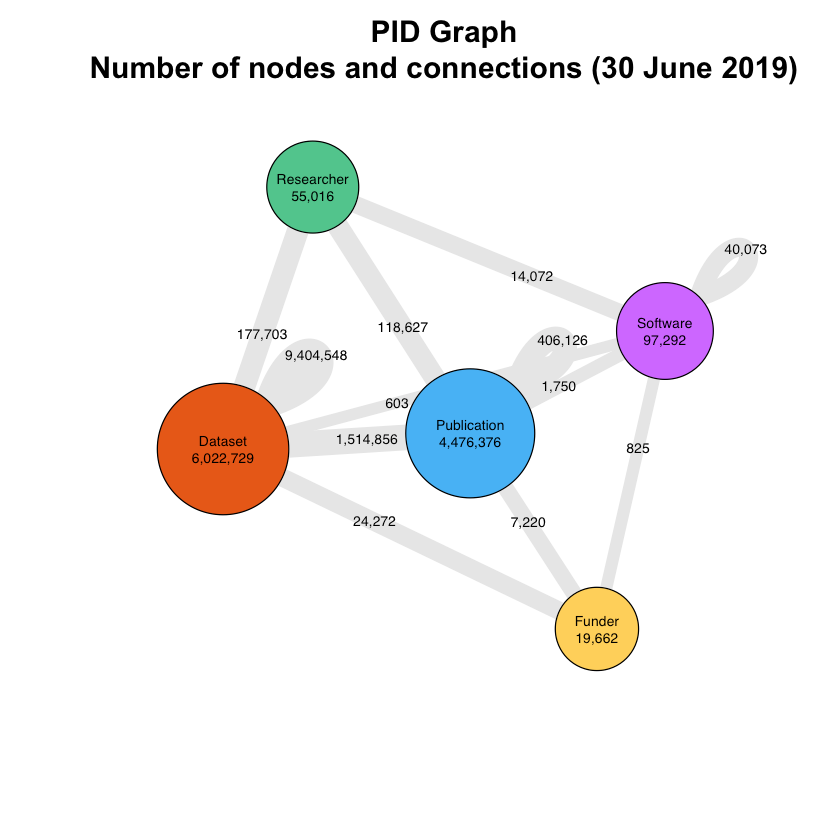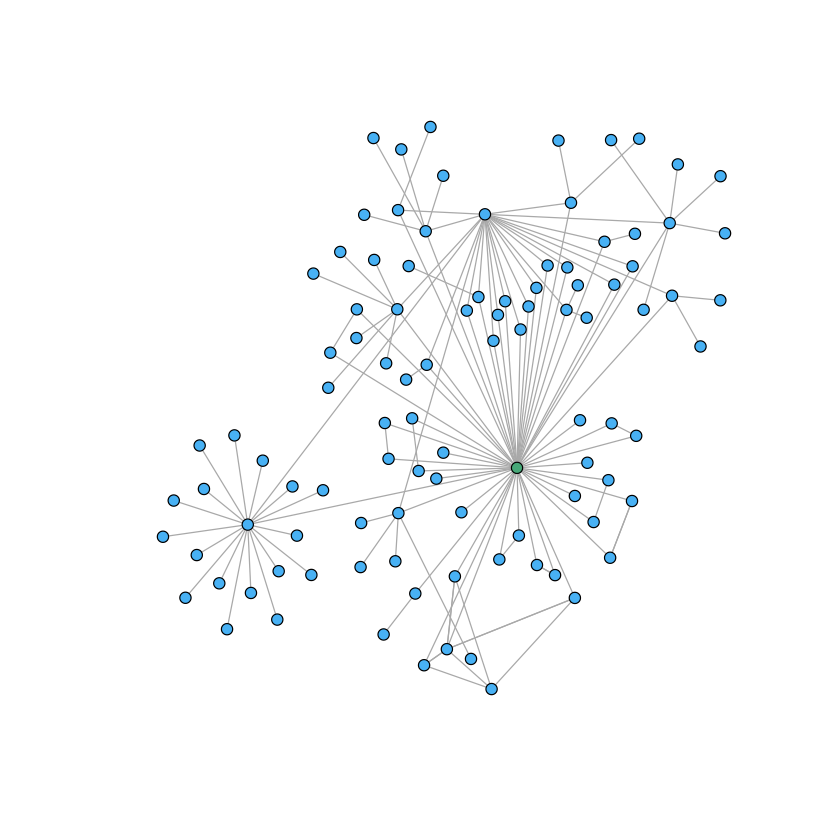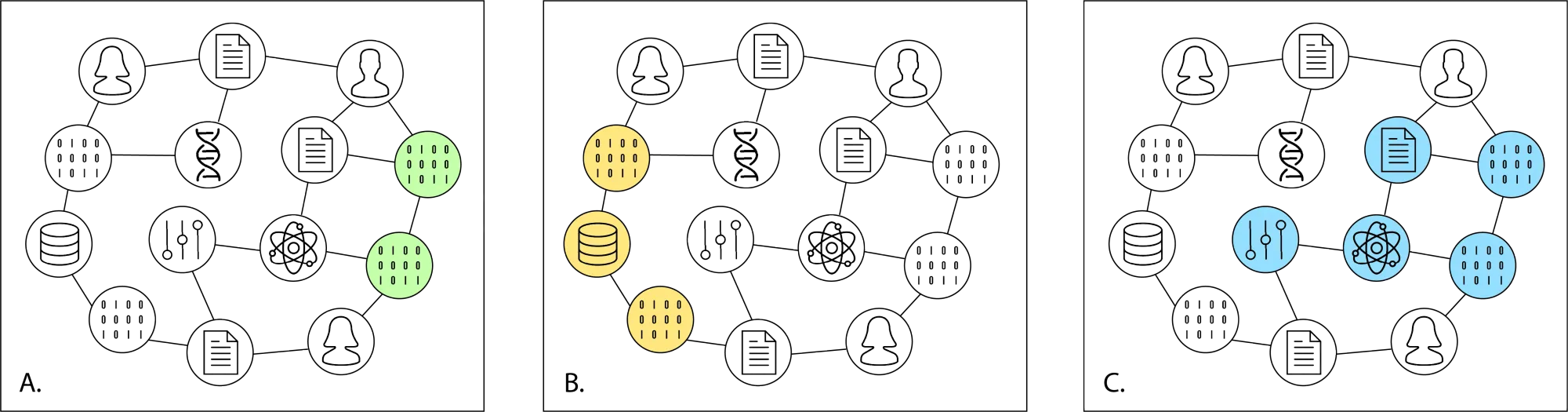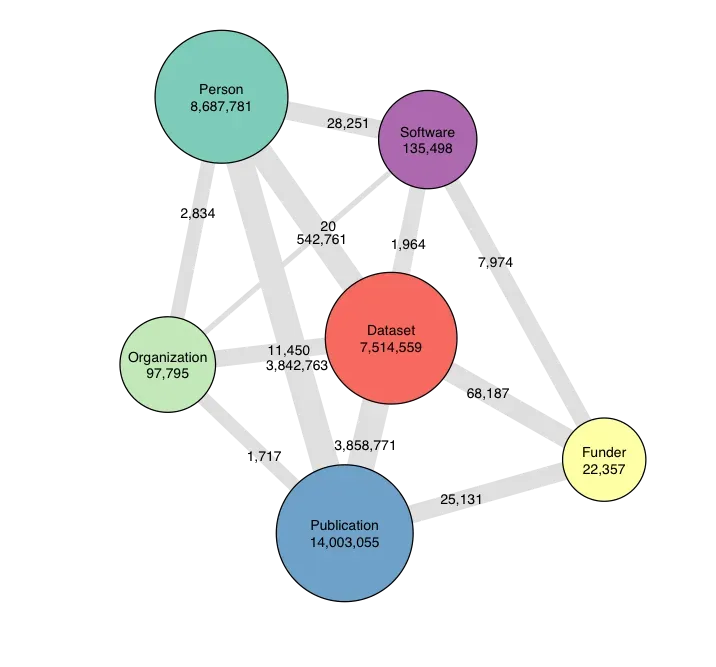
Today DataCite launches a new API that powers the PID Graph, the graph formed by scholarly resources described by persistent identifiers (PIDs) and the connections between them. The API is powered by GraphQL, a widely adopted Open Source technology that enables queries of this graph, addressing use cases of our community in ways that were not possible before.